Approximate the following integral using Gaussian quadrature with n=3. Compare your result with
the exact one
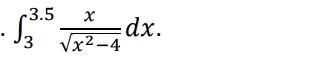
Solution:
Consider the integral
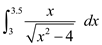
Here,
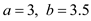
Transform the given integral into an integral over ![[-1,1]](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/d47/d47126c5-f26e-4371-8b01-fdd7a9a2cfc7/6506-4.7-2E-i105.png) by using the following transformation:
by using the following transformation:
![2x-a-b b-a ⇒x=¹[(b-a)t+a+b]= 0.251 +3.25](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/139/1391983d-6456-4a1b-acce-6b03f9113bce/6506-4.7-2E-i106.png)
This permits Gaussian quadrature to be applied in any interval![[a,b]](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/7c3/7c3aec51-f297-4906-8171-13a35472bd7a/6506-4.7-2E-i107.png) , because,
, because,
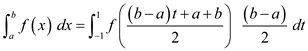
Therefore given integral transforms to,

Gaussian quadrature formula with 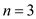 is,
is,
 …… (1)
…… (1)
Here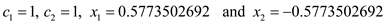 , and
, and
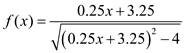
Substituting these values in (1) gives,
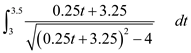
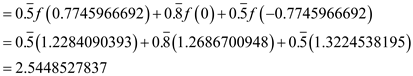
Therefore,

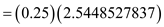
= 0.6362131959
